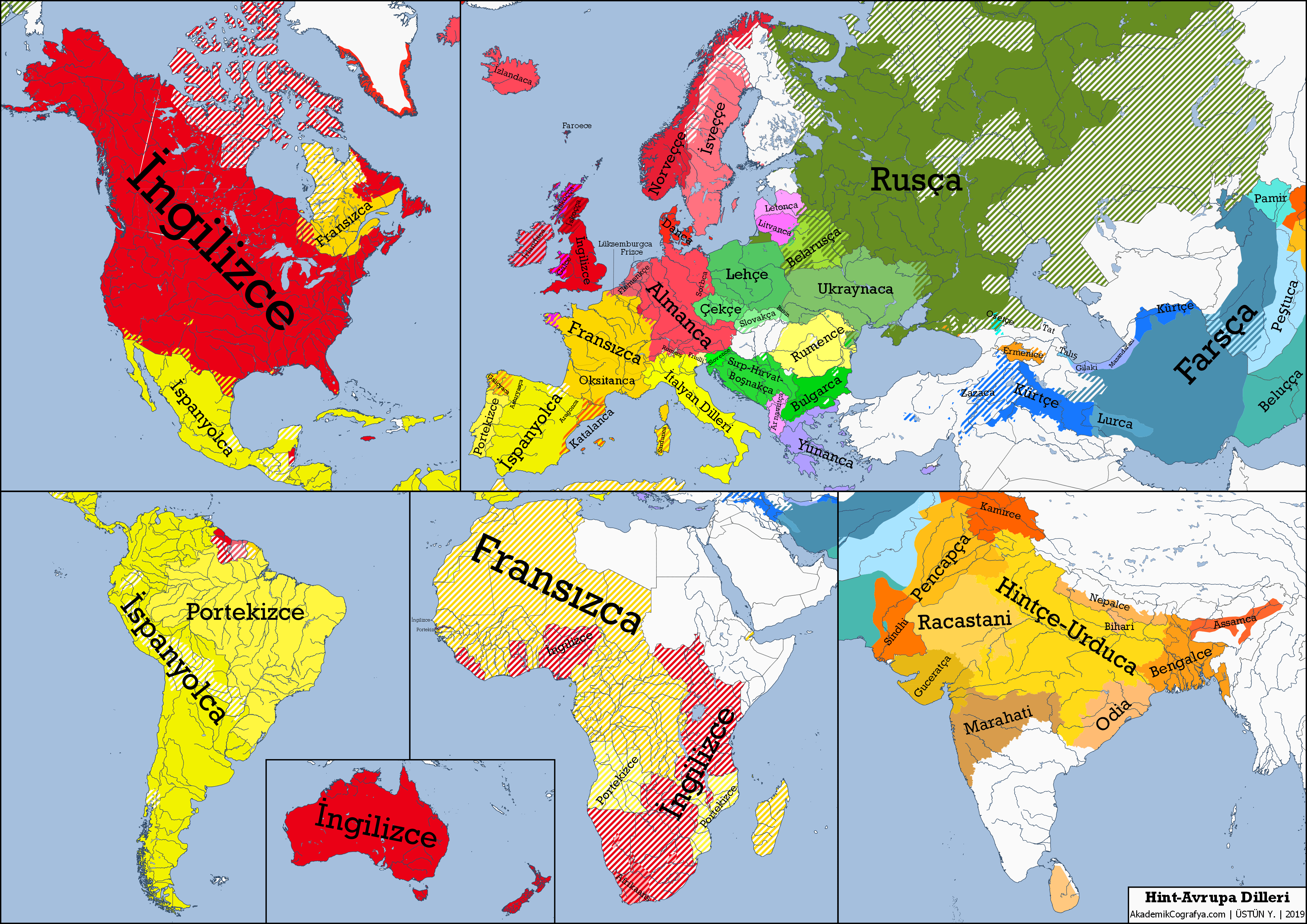
Indo-European Languages: Tracing Their Ancient Origins
The Indo-European languages represent one of the largest and most widely spoken language families in the world, encompassing over 400 distinct languages and dialects. Spoken by approximately 40% of the global population, their origins have been a topic of intense study in historical linguistics for centuries. Recent research has traced the roots of these languages to the Caucasus Lower Volga region, with genetic evidence illuminating a rich tapestry of Yamnaya ancestry dating back 6,500 years. This monumental discovery not only sheds light on language origin studies but also correlates linguistic evolution with demographic shifts in prehistoric populations. As scholars delve deeper into the relationship between genetic evidence and language development, the fascinating journey of Indo-European languages continues to unfold, revealing the intricate connections between culture and communication.
The languages of the Indo-European family, often referred to as the vast linguistic group that includes tongues like Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, have captivated linguists and historians alike. This classification points to a shared ancestry among these languages, suggesting a complex interplay of communication that spans across continents and epochs. Research into their origins has led experts to scrutinize geographical regions like the Caucasus and the Lower Volga, where significant breakthroughs in understanding Yamnaya heritage have emerged. The findings have profound implications for our comprehension of how ancient populations influenced the evolution of these languages, framing future inquiries into genetic studies and the language origin phenomena. By tracing the intertwining paths of human migration and linguistic development, we gain valuable insights into the history of human civilization.
Understanding the Origins of Indo-European Languages
The landmark studies recently published in the journal Nature shed light on the origins of the Indo-European languages, which are spoken by over 40% of the global population today. Researchers have pinpointed the Caucasus Lower Volga people, who speak an ancestor tongue dating back around 6,500 years, as the pioneers of this profound linguistic family. The study has brought forth compelling genetic evidence, showcasing the significant role that this early population played in the genesis of languages that would evolve into many modern tongues across Europe and Asia. This genetic tapestry not only highlights the linguistic connections but also the historical migrations that contributed to the rich diversity of languages we see today.
Through historical linguistics and the study of ancient DNA, researchers unravel the cultural and social frameworks that influenced language development. The historical significance of the Yamnaya people, often seen as a likely candidate for the bearers of proto-Indo-European languages, reveals a complex interweaving of genetics and linguistics, and invites further exploration into how ancient populations interacted and fused over millennia.
In examining how the Indo-European languages spread, researchers utilized advanced techniques in genetic analysis alongside linguistic reconstruction. This dual approach enabled them to visualize migratory patterns and cultural exchanges that informed the languages spoken throughout Europe and into South Asia. The findings from the Caucasus Lower Volga population not only affirm the steppe hypothesis but also provide a nuanced understanding of the linguistic relationships among diverse groups. As we delve deeper into these origins, we also encounter questions regarding the transmission of knowledge, culture, and language itself, illuminating the profound conditions under which these linguistic transformations occurred.
Genetic Evidence and Linguistic Ancestry
Recent advancements in genetic science have been pivotal in uncovering the lineage of Indo-European languages. The genetic evidence obtained from the Caucasus Lower Volga region reveals a dynamic interplay between the early speakers of these languages and their geographic neighbors. This demographic fluidity, as suggested by the mixing of populations, showcases how languages can evolve through contact and exchange rather than in isolation. The Yamnaya people, identified as key figures in this cultural evolution, reflect the importance of genetics as a tool in historical language origin studies, allowing researchers to trace the lineage of modern tongues back thousands of years.
The interplay of genetics and language underlines an intriguing aspect of human history, illustrating how innovations such as the wheel and horse domestication led to enhanced mobility. As these pastoralists migrated, they brought with them not only their livestock but also their languages and cultural practices. Linguists have noted similar syntactical structures and vocabulary across languages that trace back to these ancient proto-Indo-European roots. This provides a compelling framework for understanding the connections among languages spoken in diverse regions, from the fringes of Europe to the Indian subcontinent.
The Role of the Yamnaya in Language Dissemination
The Yamnaya culture represents a pivotal point in the study of Indo-European languages, acting as one of the primary conduits through which these languages spread across vast geographical regions. Their adeptness at harnessing the bioenergy of the Eurasian grasslands, coupled with their innovations in herding and transportation, facilitated extensive migrations and intercultural exchanges. By adopting advanced techniques, they became not only economic powerhouses but also key players in the dissemination of language. The cultural practices and social structures of the Yamnaya ensured that as they moved, so too did their language, weaving a complex tapestry of linguistic evolution.
Although their influence was profound, the legacy of the Yamnaya extends beyond mere language dissemination—it’s also about cultural integration. As they settled in new territories and interacted with indigenous populations, they fostered a melting pot of customs and linguistic traits. Understanding this shared ancestry provides powerful insights into how languages have developed uniquely while retaining roots that connect them back to common ancestors. Thus, the study of the Yamnaya’s role in language transmission not only enhances our grasp of Indo-European languages but also shapes our understanding of human history as a narrative of migration, adaptation, and cultural exchange.
Archaeological Insights into Language Origins
Archaeological findings have played a crucial role in supporting the genetic and linguistic hypotheses regarding the origins of Indo-European languages. Sites associated with the Caucasus Lower Volga people reveal burial practices and societal structures that illuminate aspects of their life, reflecting a culture deeply connected to the land. The presence of kurgans, or burial mounds, highlights the values and beliefs of these early populations, providing tangible links to their linguistic heritage. As researchers excavate these ancient sites, they uncover artifacts that suggest not only how these communities lived but also how they communicated, further bolstering the genetic findings of shared ancestry.
Moreover, archaeological evidence bridges the gap between genetic data and the historical linguistics of Indo-European families. For instance, the artifacts found in Yamnaya burial sites offer clues about their social organization and interactions with surrounding communities. This interdisciplinary approach allows for cross-validation of theories regarding migration patterns and language spread, effectively creating a more cohesive narrative about the emergence of the Indo-European languages. By piecing together both the material culture and genetic lineage, researchers can trace back the evolution of language amidst the complexities of human development over millennia.
The Linguistic Puzzle of Proto-Indo-European
Understanding the complex puzzle of proto-Indo-European languages necessitates a multidimensional approach that combines linguistics, genetics, and archaeology. This comprehensive study emerges from a long tradition of inquiry that began as early as the 18th century when scholars first noted the similarities in languages that span across continents. The findings from recent studies have provided essential insights into how these ancient languages might have originated and evolved over time. By identifying the Caucasus Lower Volga people as a significant ancestral group, researchers have effectively positioned them at the heart of an extensive linguistic lineage.
The efforts to unravel the mysteries of these languages illustrate the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration among linguists, anthropologists, and geneticists. Advances in genetic analysis have offered substantial evidence that supports and clarifies many longstanding hypotheses, such as the steppe hypothesis, which posits that the origins of these languages can be traced back to particular geographic and cultural contexts. By utilizing genetic markers and linguistic reconstructions, scholars are piecing together a narrative about human migration and the interconnectedness of language across various regions, further emphasizing the rich tapestry that shapes our understanding of linguistic ancestry.
The Impact of Cultural Traditions on Language Evolution
Cultural traditions significantly influence language evolution, as observed in the practices of the Yamnaya and their ancestors. The customs surrounding burial, social organization, and community interactions often interlace with linguistic development, marking the continuity of a people’s identity through language. For example, the shared practice of kurgan burial among the Yamnaya reflects not just their ancestral traditions but also reveals how language is transmitted as part of cultural legacy. These practices are intricately linked to their linguistic outputs, revealing how language serves as a vessel carrying cultural values and societal norms across generations.
Moreover, as scholars analyze the relationship between culture and language, it becomes clear that changes in social practices can precipitate shifts in language use and evolution. The Yamnaya’s innovations in herding and mobility signify how technological advancements can lead to both social shifts and linguistic changes. Language, therefore, is not static; it evolves in tandem with cultural traditions and interactions. The study of these dynamics provides valuable context for understanding why certain linguistic features persist or transform, placing cultural practices at the forefront of language evolution.
Exploring Genetic Footprints in Language Spread
The analysis of genetic footprints has unveiled significant migration patterns that correlate with the spread of Indo-European languages. Research from David Reich’s lab highlights how genetic markers indicate the movements of the Yamnaya people across Europe and into parts of Asia. These markers serve as a form of historical document that tracks ancestry, allowing researchers to visualize where individuals and groups intermingled throughout their migrations. This genetic evidence essentially acts as a tracer dye, revealing how languages transitioned and adapted in different regions, thus broadening our understanding of linguistic distribution.
Furthermore, genetic studies have identified the Yamnaya as a critical vector for language dissemination, leading to a demographic reshaping of regions such as ancient Germany and the Iberian Peninsula. These populations carried their languages—not just as a means of communication but as a cultural artifact that encapsulated their identity. The genetic overlaps discovered in various modern populations indicate ancestral connections that can be traced back to these migratory events. As researchers continue to analyze ancient DNA, they uncover the intricate web of human history and language that weaves together diverse cultures and civilizations.
The Future of Linguistic Research
As we look towards the future of linguistic research, the integration of genetic studies and archaeological findings promises a new era of discoveries regarding language origins. The insights gained from understanding the Caucasus Lower Volga people and their implications for Indo-European languages illustrate the potential for interdisciplinary methodologies. With technology advancing rapidly, genetic tools will likely unveil even more connections across languages and populations, revealing previously unidentified links between cultures and their languages.
Moreover, continued collaboration among linguists, geneticists, and archaeologists will foster a more holistic understanding of how languages develop and change over time. As researchers delve into complex questions regarding the relationships among ancient populations, the interplay between culture, language, and genetics will inevitably shape the path forward in linguistic studies. The collective efforts to decode these enigmatic connections will enhance our appreciation for the rich histories embedded within languages and their speakers, ultimately contributing to a deeper understanding of human civilization.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Indo-European languages and their significance?
Indo-European languages are a family of over 400 languages spoken by more than 40 percent of the global population. This linguistic family includes many modern languages, such as Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, and is critical for understanding cultural and historical linguistics across Europe and Asia.
How does the study of Yamnaya ancestry contribute to understanding Indo-European languages?
The Yamnaya people, identified as key figures in the dissemination of proto-Indo-European languages, offer crucial insights into the linguistic evolution and migration patterns of Indo-European speakers. Their legacy reveals the genetic and cultural interconnections that shaped modern languages.
What role does historical linguistics play in studying the origins of Indo-European languages?
Historical linguistics employs methods to compare languages and trace their evolution, helping researchers pinpoint the origins of Indo-European languages. Studies incorporate linguistic reconstructions alongside genetic evidence from archaeological findings to understand how languages spread.
What is the significance of genetic evidence in the study of Indo-European origins?
Genetic evidence, such as DNA analysis from ancient populations, supports hypotheses in language origin studies. This evidence helps link populations like the Caucasus Lower Volga and Yamnaya to the early speakers of Indo-European languages, demonstrating their migration and cultural impacts.
How did the Caucasus Lower Volga people influence Indo-European languages?
The Caucasus Lower Volga people are believed to be the original source of Indo-European languages, mixing with other groups and spreading their linguistic heritage across the Eurasian steppe to Europe and beyond, thereby shaping the linguistic landscape we study today.
Why is the study of Yamnaya culture important for understanding language and genetics?
Yamnaya culture is pivotal as it represents early pastoralist societies that contributed to the spread of Indo-European languages. Understanding their cultural practices, including burial traditions and genetic mixing, enriches our knowledge of how languages evolved and dispersed.
What methods are used in language origin studies related to Indo-European languages?
Research in language origin studies combines historical linguistics, archaeological evidence, and genetic analysis. These interdisciplinary methods allow scholars to reconstruct the pathways through which Indo-European languages developed and spread over millennia.
How do ancient burial practices inform our understanding of Indo-European ancestry?
Ancient burial practices, such as kurgans used by the Yamnaya, provide archaeological insights that help reconstruct the social and cultural dynamics of early Indo-European speakers. These practices may reveal connections to their language and migrations within the region.
What challenges do researchers face when studying Indo-European languages?
Researchers encounter challenges such as limited access to historical records, the need for interdisciplinary collaboration, and contemporary geopolitical issues, which can hinder the collection of genetic and archaeological data from specific regions relevant to Indo-European studies.
What implications do the findings about Indo-European origins have for modern linguistics?
Findings about the origins of Indo-European languages enhance our understanding of language development and migration patterns. This knowledge propels current linguistic research and offers perspectives on how languages relate, evolve, and influence one another across different cultures.
| Key Study Points | |
|---|---|
| Origin of Indo-European languages | 6,500 years ago, in present-day Russia, among the Caucasus Lower Volga people. |
| Significance of findings | Sheds light on the origins of over 400 languages spoken by 40% of the world. |
| Yamnaya Culture | Nomadic pastoralists who spread the Indo-European languages across Europe and into Asia. |
| Research collaboration | Involves geneticists, linguists, and archaeologists, resulting in a unified genetic picture of Indo-European languages. |
| Cultural practices | Yamnaya and their ancestors buried their dead in kurgans, preserving their history. |
Summary
Indo-European languages represent a rich linguistic tapestry that connects a substantial portion of the global population. Recent findings emphasize the historical significance of the Caucasus Lower Volga people, identified as the source of many languages we speak today. Unraveling this origin provides invaluable insights into not only linguistic developments but also the cultural practices that shaped early human societies across Europe and Asia.